The Cyber Crime Magazine defines Cybercrime as the “damage and destruction of data, stolen money, lost productivity, theft of intellectual property, theft of personal and financial data, embezzlement, fraud, and post-attack disruption to the normal course of business, forensic investigation, restoration and deletion of hacked data and systems, and reputational harm.”
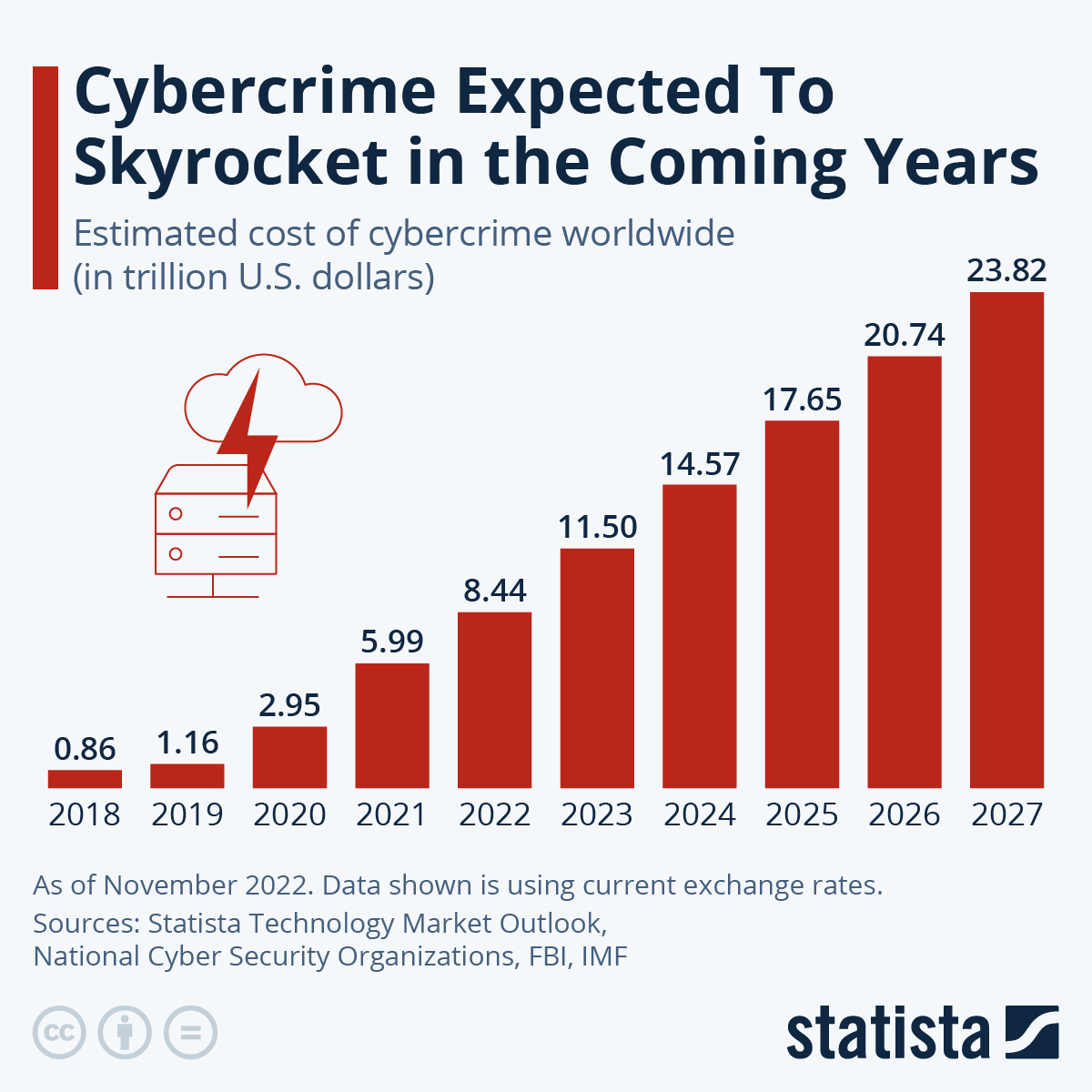
Estimates from Statista’s Cybersecurity Outlook suggest that the global cost of cybercrime is expected to rush in the next five years. According to the estimation it is going to rise from $8.44 trillion in 2022 to $23.84 trillion by 2027.
There are more potential opportunities for cyber criminals to
exploit as people are switching to online platform whether it is for work or their
personal lives. With the spread of online commerce, techniques used by
attackers have also become more advanced and more tools are available to help scammers.
The coronavirus pandemic saw a particular shift in cyber-attacks,
as Statista’s Outlook analysts explain:
“The COVID-19 crisis led to many organizations facing more cyber-attacks due to the security vulnerability of remote work as well as the shift to virtualized IT environments, such as the infrastructure, data, and network of cloud computing.”
Infographic by: statista